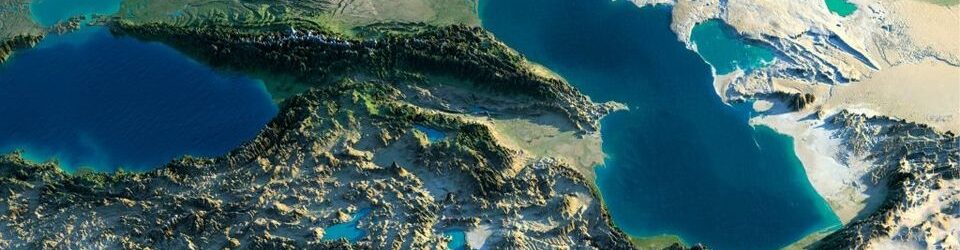
Water has always been a major cause of wars and border conflicts in the Central Asian region. For being one of the greatest geographical regions, Central Asia has limited water resources. The modern history of the region has been fueled with various ethnic and territorial clashes. Apparently, the main catalysts behind conflicts have been attempts to take control of rich water resources. The main sources of water in Central Asia are the Syr Darya and Amu Darya Rivers, mostly fed by snow- and glacier melt from the Pamir, Hindu Kush, and Tien Shan mountain ranges. The 2,200-kilometer Syr Darya originates in the Tien Shan, flows through Kyrgyzstan as the Naryn River, and combines with the Kara Darya to become the Syr Darya.
The water resource crisis is not a new phenomenon in Central Asia. With the eventual fall of the Soviet Union, the resource-sharing system is imposed on the region totally disintegrated. The root of the problem is that the main water resources in Central Asia flow from territories of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. Kyrgyzstan holds the rule of downstream Syr-Darya flow at the Toktogul dam, while Tajikistan re-launched the building of Rogun dam on Vakhsh River, which was then shut down due to lack of funds and strained relations with neighboring Uzbekistan. If completed, the Rogun dam will be able to ensure mountainous Tajikistan electricity, as it is in need of energy. Despite its quite favorable location in an energy-rich region, the Central Asian country faces energy-related problems. Continue reading